The parabola is one of the primary conic sections. In any engineering or mathematics application, we'll see a lot of applications:
- Describing projectile trajectory
- Designing vertical curves in roads and highways
- Making reflectors and telescope lenses.
These are a few examples of its many uses. For now, let's learn more about the basic geometry of the parabola:
Locus Definition
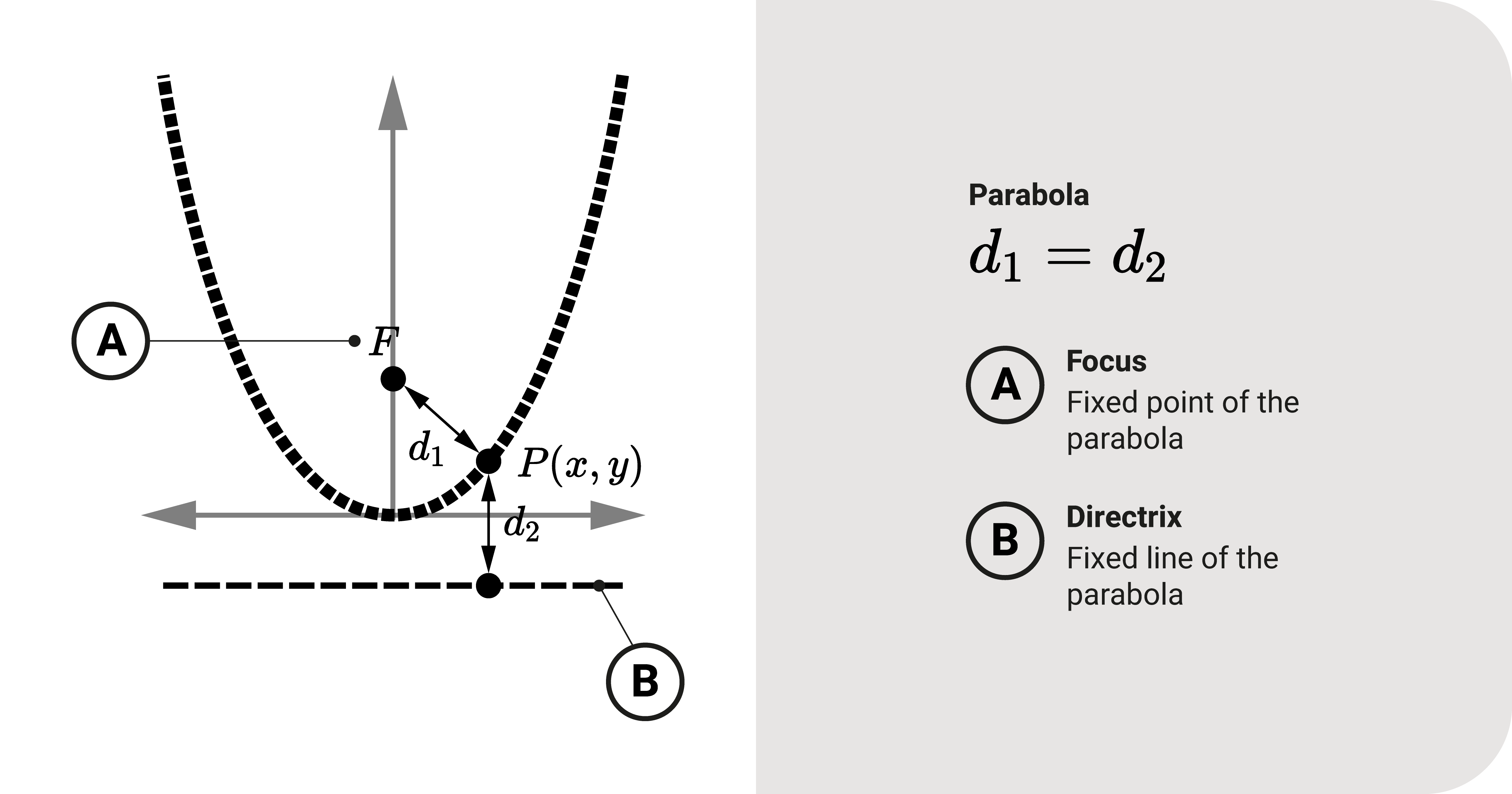
At its basic, it is a set of all points that is equidistant to:
- A fixed point \(F\) called the focus,
- A fixed line called the directrix.
To expand, let's consider a point \((x, y)\) as shown in the figure. The distance \(d_1\) between this point and \(F\) should be equal to its perpendicular length \(d_2\) to the directrix.




